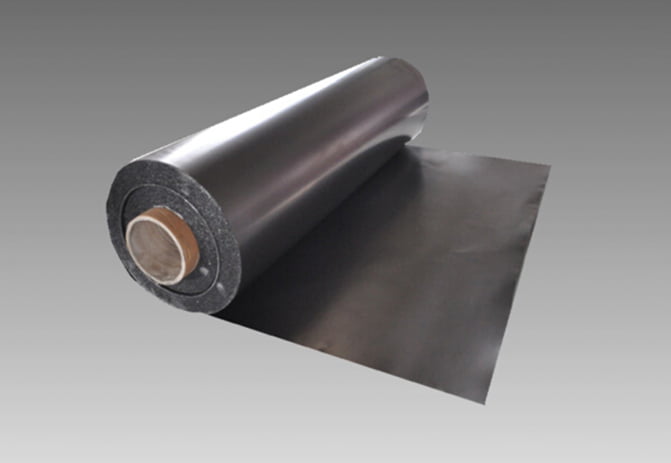
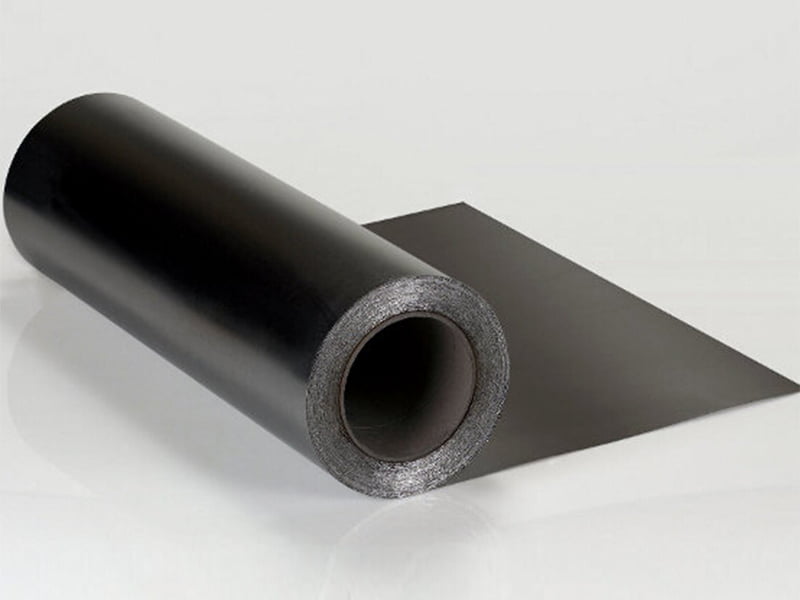
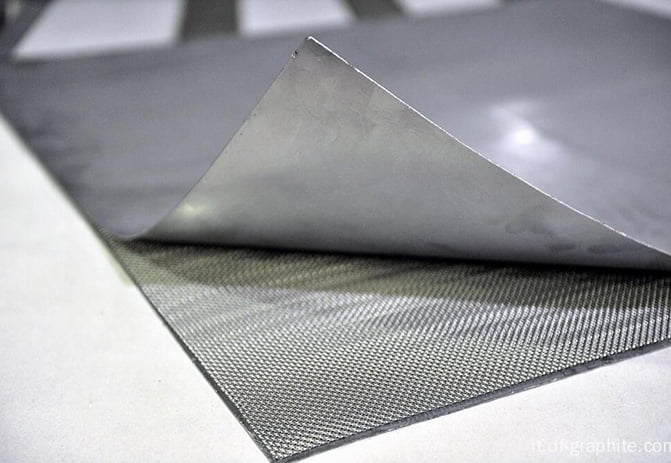
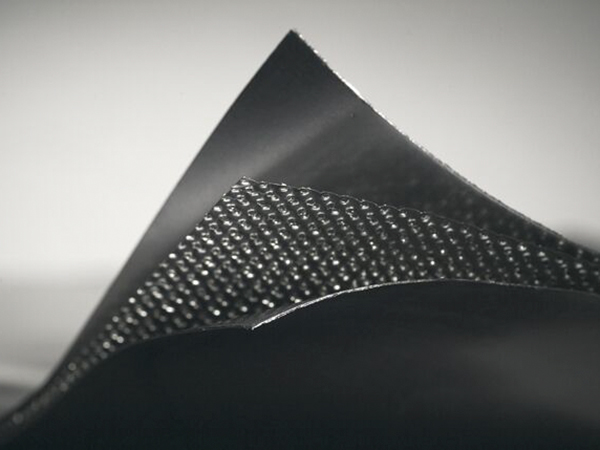
1. **TOP SEALING Graphite Sheet**: This is likely a brand or type of gasket material that uses graphite as its primary component. Graphite is chosen for its excellent heat resistance, chemical stability, and good sealing properties.
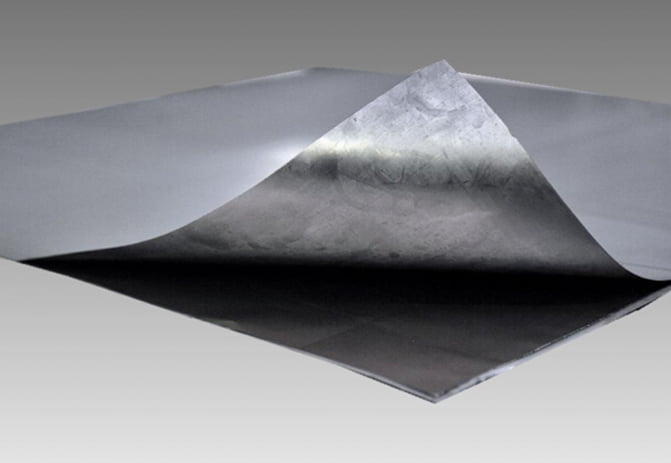
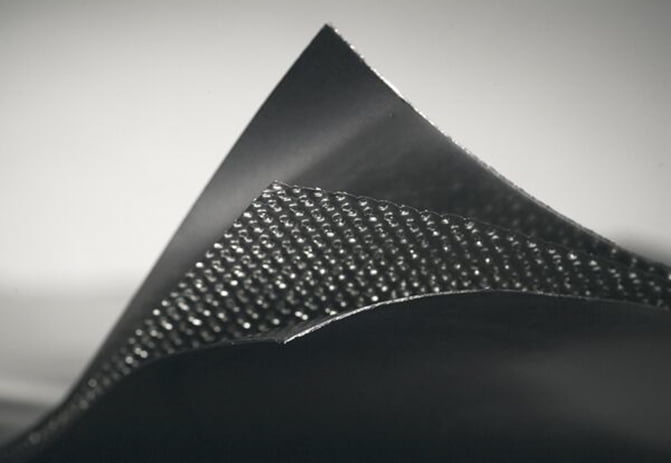
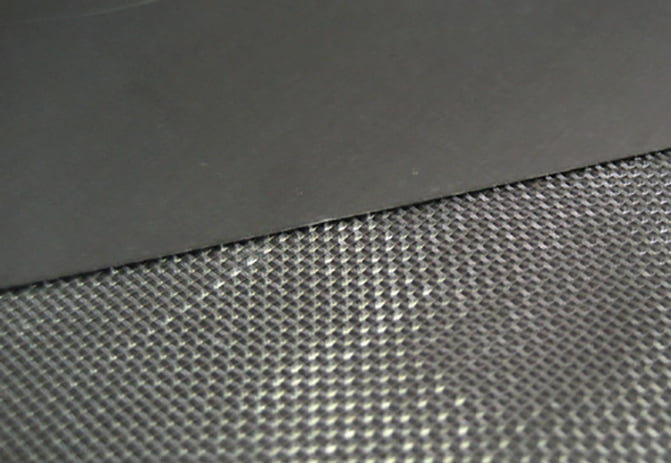
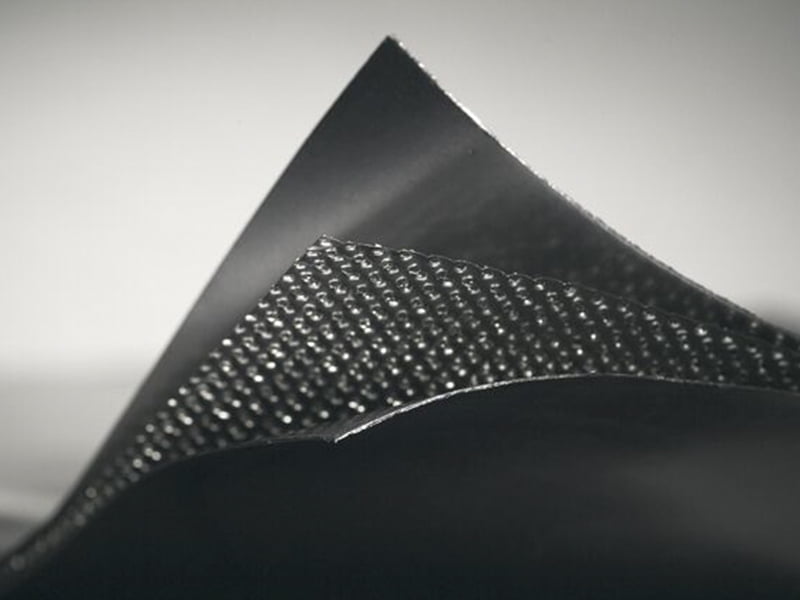
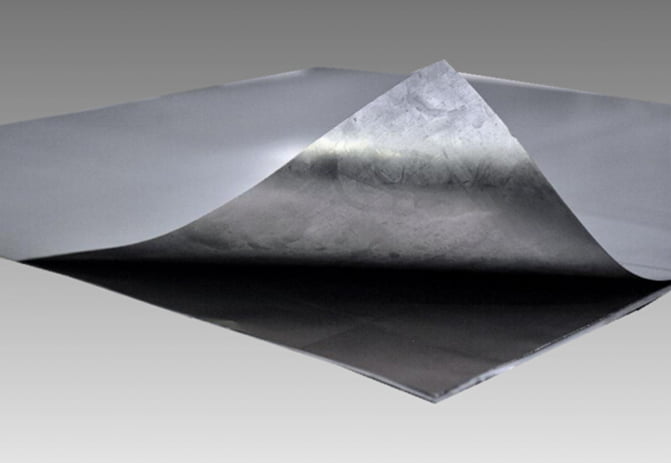
2. **Pure Expanded Graphite Plates**: These are the two outer layers of the gasket. Expanded graphite is a form of graphite that has been treated to expand its volume, making it lightweight and porous. This expansion improves its sealing properties and makes it suitable for use as a gasket material.
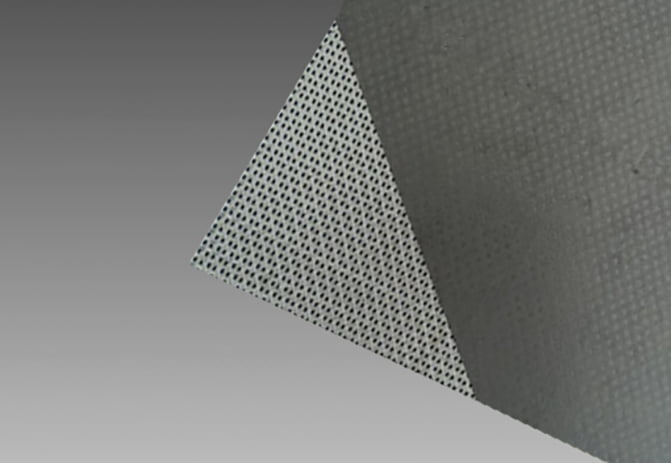
3. **Metal Core**: The core of the gasket is a thin metal layer that provides structural support and helps maintain the shape of the gasket. The thickness of 0.1 mm is quite thin, which is typical for a metal core in a composite gasket to ensure flexibility and conformability to flange surfaces.
4. **Stainless Steel Material**: The metal core can be made from different types of stainless steel, which are chosen for their corrosion resistance and strength. The options provided are:
- **SS316L**: A type of stainless steel that is particularly resistant to pitting and crevice corrosion, making it suitable for use in more corrosive environments.
- **SS304**: A more common type of stainless steel that provides good general corrosion resistance.
5. **Carbon Steel**: This is a steel that is not alloyed with other elements to a great extent, making it more cost-effective but potentially less resistant to corrosion than stainless steels.
6. **Nickel 600**: A high-performance alloy that is known for its excellent resistance to corrosion, particularly in high-temperature environments. It is often used in applications where the gasket will be exposed to aggressive chemicals or high temperatures.
The choice of material for the metal core and the type of expanded graphite used can depend on the specific application requirements, such as the type of fluid being sealed, the temperature and pressure conditions, and the chemical compatibility of the materials with the process environment.